Geochemical Baseline Mapping of Soils Developed on Diverse Bedrock from Two Regions in Croatia
Main Article Content
Abstract
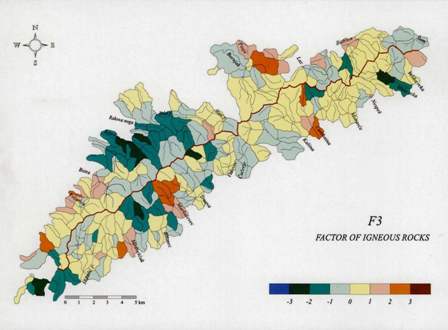
The comparison of contents and distribution maps for Al, As, Ba, Ca, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, La, K, Na, Ni, Mg, Mn, P, Pb, Sc, Sr, Ti, Th, V, Y, Zn and Hg in the topsoil cover of two typical regions are given. One is a carbonate bedrock (karst) dominated region (southern Dalmatia) and the other a non-carbonate bedrock dominated region (NW Croatia). The results imply that the soils developed on carbonate bedrock have higher mean values of almost all elements excluding K, Na, Mg and Ba, which are lower in carbonate terrains. In comparison with the non-carbonate terrains, for the carbonate terrains the following elements have higher mean concentrations: Al, As, Co, Cu, Fe, La, Mn, Pb, Ni, Mn, Th, V, Cr, Zn, Zr and Nb, while Sr, P and Ti have similar contents. Approximately 4% of the sites can be considered as moderately enriched (polluted) in Pb, either from mining activities or airborne deposition. Only a limited number of sampling sites can be directly linked with mineralization. The derived factors are usually interpreted as associations of elements that imply a common source or behavior in regard to geogenic or anthropogenic influences. It was found that difference between the northwestern Croatia and southern Dalmatia is not expressed only by concentration differences but also by element associations. Five factor models accounting most of the data variability seemed appropriate to portray the geochemical variability within the topsoil of both regions
Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Article Details
Issue
Section
Original Scientific Papers
Authors have copyright and publishing rights on all published manuscripts.