Recent Tectonic Activity in the Imotsko Polje Area
Main Article Content
Abstract
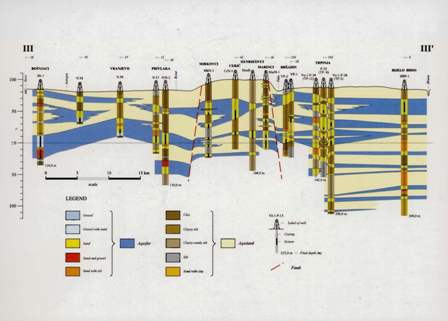
Displacements of the Adriatic microplate, particularly of itssouthern part, are of crucial importance for the understanding ofrecent tectonic movements. Deformations of the structural fabric andthe resulting tectonic activity also encompass the studied area. Thereare four most active fault zones - Mosor-Biokovo, Zagvozd-Vrgorac-Metkoviæ, Trilj-Tihaljina-Èapljina and Imotski-Meðugorje-Popovopolje. In the explored area, these zones delimit the Imotsko polje.The calculated regional stress is oriented in the range between10-190¡ and 350-170¡. The relationship between the orientation ofstructural units and stress enables reverse displacements, most frequently in the direction of the south and south-east. The change instress orientation in the Mt. Biokovo hinterland makes the aforementioned fault zones surrounding the Imotsko polje favourably oriented in respect to the stress, thus enabling dextral horizontal tectonic transport of the structures in different fault blocks.In the two fault zones - Trilj-Tihaljina-Èapljina and Imotski-Meðugorje-Popovo polje, there are 98 outcrops suitable for the structuralgeology measurements. The obtained data on the local stress orientation and spatial displacement of structures are the most important.The character of faults and the most active fault sections are marked,as well as the local structures that are formed due to strong horizontalcomponent of structural displacement in the studied fault zones.Recent tectonic activity is confirmed by the occurrence of earthquakes.Spatial distribution of the earthquake epicentres depicts zonesof seismotectonic activity that are related to the aforementioned mostimportant fault zones. Two of the fault zones - Trilj-Tihaljina-Èapljinaand Imotski-Meðugorje-Popovo polje are especially well markedby earthquakes occurring at depths of between 3 and 15 km.
Article Details
Issue
Section
Original Scientific Papers
Authors have copyright and publishing rights on all published manuscripts.